In today’s dynamic entrepreneurial landscape, securing adequate funding remains one of the most critical challenges for startups worldwide. With global venture capital investment reaching $120 billion in Q3 2025 and AI companies capturing over 51% of total venture funding, the fundraising environment has never been more competitive. However, understanding the diverse funding options available can significantly increase a startup’s chances of success. While statistics show that only 2-3% of pre-seed applications receive external funding, founders who strategically leverage multiple fundraising channels can dramatically improve their odds. This comprehensive guide explores the top five proven methods for startup fundraising globally, providing entrepreneurs with actionable insights to secure the capital they need to transform their vision into reality.
1. Venture Capital Funding: The Traditional Powerhouse
Venture capital remains the cornerstone of startup funding for high-growth companies seeking substantial capital injections. Venture capital firms provide not only financial resources but also strategic guidance, industry connections, and operational expertise that can accelerate a startup’s trajectory. The venture capital funding model operates through a structured progression of rounds—from seed funding to Series A, B, C, and beyond—each designed to support specific growth milestones.
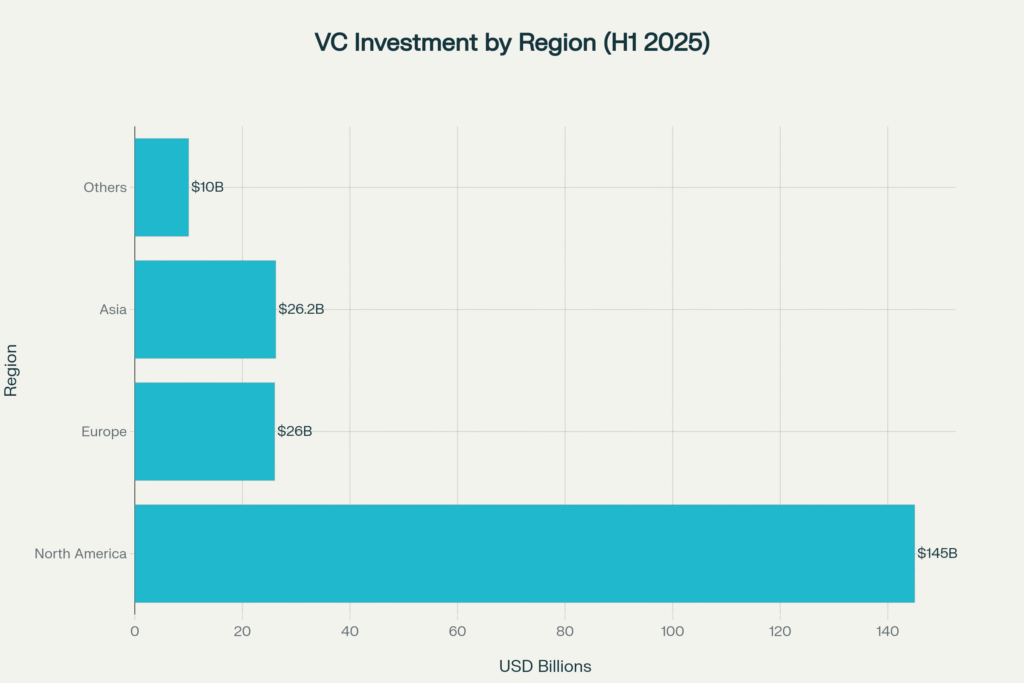
Global venture capital investment distribution across major regions in the first half of 2025, showing North America’s dominance with $145B in funding
Understanding the VC Funding Rounds
The venture capital journey typically begins with seed funding, where startups can raise between $500,000 to $5 million from angel investors and early-stage VC firms. This initial capital helps entrepreneurs develop their minimum viable product (MVP), conduct market testing, and hire key team members. Following successful seed rounds, startups that demonstrate strong business models and revenue potential can progress to Series A funding, where they typically raise $2 million to $15 million.
Series A funding marks a critical milestone in a startup’s journey, representing the transition from initial seed funding to more substantial institutional investment. At this stage, venture capital firms conduct rigorous due diligence, evaluating the startup’s growth potential, market opportunity, revenue generation capabilities, and scalability. Companies that successfully navigate Series A face even higher expectations at Series B, where valuations increase and investors demand proven financial performance and sustainable growth metrics.
By the time startups reach Series C funding and beyond, they typically seek $25 million to $100 million or more to develop new products, expand globally, acquire competitors, or prepare for an initial public offering. At this late stage, hedge funds, private equity firms, and investment banks join venture capital firms as key investors, reflecting the reduced risk and higher valuations of more mature companies.
Geographic and Sectoral Trends
North America continues to dominate the global venture capital landscape, capturing approximately 70% of worldwide funding in H1 2025, with $145 billion invested in U.S. and Canadian companies—a 43% year-over-year increase. The United States leads not only in volume but also in concentration, with eight of the top ten global deals originating from American companies. Europe has shown more modest growth, with VC investment reaching $26 billion, while Asia raised $26.2 billion, though this represents a decline from previous years.
The artificial intelligence sector has emerged as the dominant force in venture capital, with AI companies capturing 51% of total venture funding in 2025—marking the first year AI startups have claimed the majority of funding. Within the AI ecosystem, industrial humanoid robots recorded 17 deals in Q3 2025, making it one of the most active market segments. This sectoral concentration demonstrates how investor priorities are shifting toward transformational technologies with massive market potential.
Success Rates and Strategic Considerations
While venture capital offers substantial benefits, entrepreneurs must understand the competitive nature of this funding channel. Top-tier VC firms often cite a 1-in-400 ratio, funding just 0.25% of deals they review. Even prestigious accelerators like Y Combinator, which receives over 10,000 applications every three months, maintains only a 1% acceptance rate. Furthermore, less than 10% of startups that secure seed funding successfully advance to Series A, highlighting the challenging progression through funding stages.
For startups that do secure venture capital, the benefits extend far beyond financial resources. VC-backed startups demonstrate significantly higher success rates, with research from Harvard Business School showing that angel-funded startups are more likely to remain in business longer, experience substantial growth, and achieve greater rates of return. In the seed stage, VC-backed startups show success rates of 55% compared to 25% for non-VC-backed companies, largely due to critical funding for research and development.
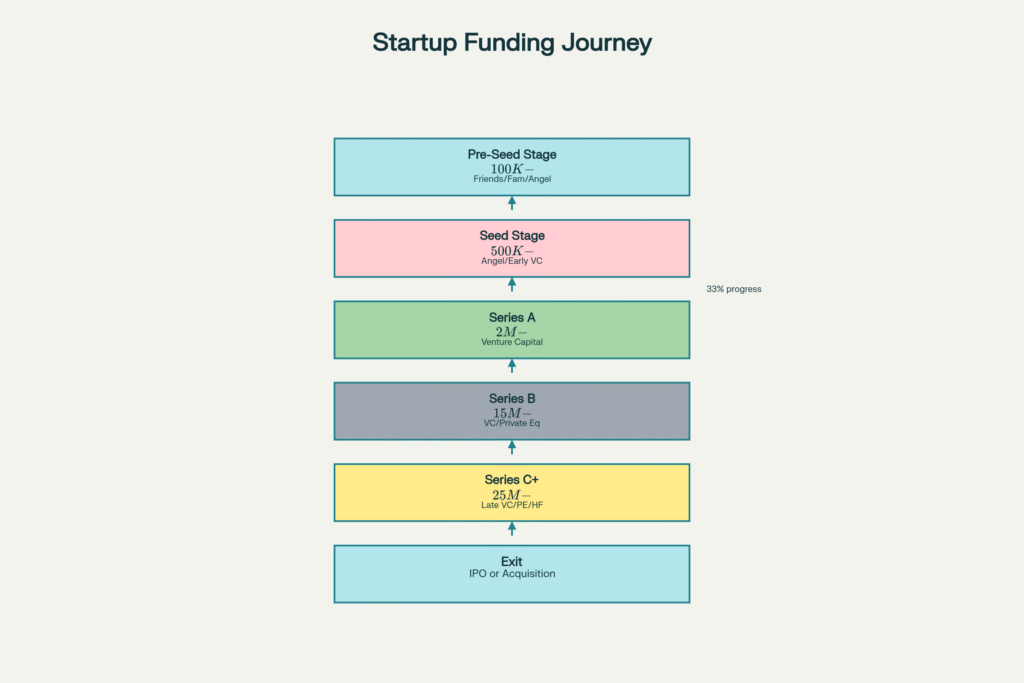
The typical startup funding journey showing progression from pre-seed through exit, with funding amounts and investor types at each stage
Checkout Our Latest Services

Brand Kit (Covered Everything)

Govt Grants Application Package (1 Year)

Govt Grant Application (6 Months Package)

Government Grant Application (Per Scheme)
2. Angel Investors: Early-Stage Capital with Mentorship
Angel investors represent a vital source of early-stage funding for startups, particularly during the critical pre-seed and seed phases when traditional venture capital may be difficult to access. These wealthy individuals provide capital to startups in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity, typically investing once or in consecutive rounds when most institutional investors are unprepared to back unproven companies.
The Angel Investment Model
Angel investors typically invest in the $25,000 to $2 million range, filling the crucial funding gap between friends-and-family rounds and more robust venture capital financing. According to statistics, angel investors provided nearly $23 billion in funding for over 67,000 startup ventures annually in the United States alone, contributing to the creation of 274,800 new jobs in 2012. In 2013, approximately 41% of tech sector executives named angel investors as a primary means of funding.
Unlike traditional lenders, angel investors operate within a fundamentally different framework. They provide capital in exchange for an equity stake in the company, meaning entrepreneurs are not obligated to repay the funds if the venture fails. This risk-sharing arrangement makes angel investment particularly attractive for early-stage startups that lack the revenue history or collateral required for traditional bank loans.
Beyond Capital: The Value-Add Proposition
What distinguishes angel investors from other funding sources is their willingness to provide more than just money. Many angels are retired entrepreneurs or executives who bring years of experience, industry expertise, and valuable networks to their portfolio companies. These investors often seek involvement that goes beyond pure monetary returns, desiring to mentor the next generation of entrepreneurs, stay abreast of current business developments, and leverage their experience on a flexible basis.
Research demonstrates the tangible benefits of angel backing. Scientists from Harvard Business School found that ventures backed by angel investors are more likely to succeed, remain in business longer, experience substantial growth, and witness greater rates of return compared to companies reliant on other forms of initial financing. The study concluded that “angel funding is positively correlated with higher survival, additional fundraising outside the angel group, and faster growth measured through website traffic”.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While angel investors offer numerous advantages, entrepreneurs must carefully consider the implications. Angel investors typically expect a rate of return equal to 10 times their original investment within the first 5-7 years. This high expectation reflects the significant risk they undertake by investing in unproven companies. Additionally, angel investors usually take an active role in company decision-making, expecting influence over strategic choices that affect the organization’s outcome.
The equity exchange component means that while entrepreneurs aren’t obligated to repay capital if the venture fails, they are essentially giving away a portion of their future net earnings. The percentage of ownership requested by angel investors typically depends on the investment amount, creating a delicate balance between securing necessary capital and maintaining meaningful founder ownership.
Angel Investment Ecosystem
Angel investors increasingly organize themselves into angel groups or angel networks, allowing them to share investment capital, pool expertise, and provide comprehensive advice to portfolio companies. This collaborative approach has grown significantly since the mid-20th century, with platforms like AngelList facilitating online equity crowdfunding and connecting investors with promising startups.
In India specifically, the angel investment landscape has flourished, with numerous active angel investors providing seed money and assistance to startup companies in exchange for ownership stakes. Angel funds typically invest in early-stage startups in exchange for equity stakes, exiting once the startup achieves maturity—often by selling to venture capitalists or private equity firms. The minimum investment in angel funds in India is Rs 25 lakh, classified as a Category 1 Alternate Investment Fund.
3. Crowdfunding: Democratizing Access to Capital
Crowdfunding has emerged as a revolutionary funding mechanism that democratizes access to capital by enabling startups to raise money from a large number of individuals, often through specialized online platforms. This funding approach has gained tremendous momentum, with platforms like Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and StartEngine collectively raising billions of dollars for thousands of startups worldwide.
The Crowdfunding Landscape
The crowdfunding ecosystem encompasses multiple models, each suited to different types of startups and funding objectives. Rewards-based crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter operate on an all-or-nothing funding model, where campaigns must meet their funding goals to receive pledged money. Since its inception in 2009, Kickstarter has funded over 250,000 projects, boasting one of the largest and most active backer communities globally. This approach works particularly well for creative endeavors, consumer products, and technology projects where backers receive early access to products or special rewards in exchange for their support.
Equity crowdfunding represents a more sophisticated approach where investors receive actual ownership stakes in the company in exchange for their funding. StartEngine has emerged as a dominant force in U.S. equity crowdfunding, helping startups raise over $1.2 billion across more than 1,000 rounds, with access to over 1.8 million potential investors. The platform enables both accredited and non-accredited investors to participate, making it accessible to a broad audience. Notably, Atombeam achieved the fastest StartEngine raise to reach a $20 million milestone in 2025.
Platform-Specific Advantages
Different crowdfunding platforms offer unique benefits tailored to specific startup needs. Indiegogo provides flexible funding options, allowing entrepreneurs to choose between all-or-nothing and flexible funding goals, where they receive pledges regardless of whether they meet their target by the deadline. With over 19,000 campaigns launching monthly since its 2008 launch, Indiegogo has become one of the most popular crowdfunding websites globally.
For startups anticipating venture capital investment due to rapid growth, Wefunder stands out with an impressive 86% project success rate. In 2025, Geoship raised $1,210,602 through Wefunder, exceeding its $100,000 minimum target by over 1,200%. Wefunder offers both equity and debt crowdfunding options, providing flexibility for startups with different capital structures and repayment capabilities.
CircleUp specializes in equity crowdfunding for consumer brands, combining funding with data-driven insights to connect startups with genuinely interested investors. The platform has helped over 500 companies raise $390 billion, demonstrating the significant capital available through specialized crowdfunding channels.
Crowdfunding Best Practices
Successful crowdfunding campaigns require more than just a good idea. According to industry experts, crowdfunding works best when paired with strong branding, a compelling founder story, and a clear delivery timeline. For consumer products, crowdfunding offers the additional benefit of validating demand and generating early revenue before launching full-scale operations.
Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo are particularly effective for consumer products, allowing startups to test market interest through product pre-orders before committing to large-scale manufacturing. This validation aspect makes crowdfunding especially valuable for entrepreneurs who want to minimize risk by confirming customer demand before investing heavily in production infrastructure.
Global Reach and Regional Variations
While many crowdfunding platforms operate globally, some focus on specific regions or markets. Crowdcube serves as a leading UK-based equity crowdfunding platform with access to European Union markets, hosting over 6,500 investors. For Australian and New Zealand startups, Equitise provides specialized equity crowdfunding services, having raised $75 million from 55,000 investors across 20,000 investments.
In India, the crowdfunding landscape includes platforms like Pepcorns, Milaap, Fueladream, and LetsVenture, offering various crowdfunding models tailored to the Indian market. These regional platforms understand local regulatory requirements, investor preferences, and market dynamics, making them valuable options for startups operating in specific geographic markets.
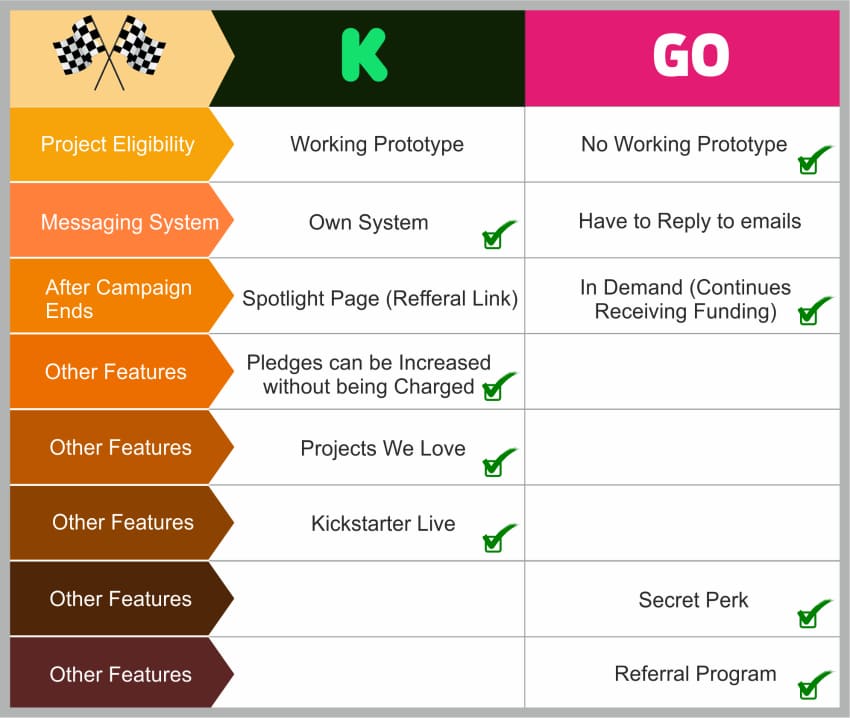
Comparison between Kickstarter and Indiegogo crowdfunding platforms highlighting key features and post-campaign benefits
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Equity crowdfunding platforms must navigate complex regulatory frameworks, particularly in the United States where Regulation Crowdfunding (Reg CF) allows companies to raise up to $5 million from the public. While this process is more streamlined than traditional methods of raising funds from accredited investors, it still requires strict financial and legal compliance. Startups pursuing equity crowdfunding should expect increased legal requirements, more rules and regulations, and potentially higher platform fees ranging from 5-12% based on the investment method.
4. Bootstrapping: Building Through Self-Reliance
Bootstrapping represents a fundamentally different approach to startup funding, where entrepreneurs build their businesses using personal savings, revenue generated by the business, or minimal external capital. This self-funding method emphasizes internal strength, self-help, and financial discipline, compelling entrepreneurs to become creative and resourceful with limited resources.
The Bootstrapping Philosophy
At its core, bootstrapping involves financing a business through personal savings, recent revenue, or resources from friends and family, without relying on traditional venture capital or external investors. Statistics reveal that 77% of small businesses in the United States start with personal savings or funds from family and friends, and approximately 78% of startups are self-funded. In Germany, almost three-quarters of startups are bootstrapped, funded by the founder’s savings or personal loans rather than venture capital.
The term “bootstrapping” stems from the metaphor of pulling oneself up by one’s bootstraps, perfectly capturing the essence of starting and growing a business using only available resources. This approach typically utilizes multiple financing instruments including entrepreneur capital, family and friends capital, bank loans, supplier loans, leasing, and subsidies.
Strategic Advantages
Bootstrapping delivers several compelling advantages that make it attractive for certain types of startups. Full ownership and control represent the most significant benefit, as founders retain 100% equity in their company without dilution from external investors. This complete ownership means entrepreneurs enjoy the full return from their business, which can be reinvested to fuel growth. When startups accept outside funding, they give up a portion of the company and often cede decision-making authority to investors who expect returns and may demand influence over strategic choices, hiring decisions, and product launches.
Financial discipline emerges naturally from bootstrapping, as limited resources force founders to manage money efficiently with unwavering focus on cash flows and reserves. This constraint often leads to better products and services, as entrepreneurs must think critically rather than rack up expenses. Bootstrapped businesses typically stay lean, avoid high fixed costs, and ensure every penny spent maximizes return. This operational efficiency contrasts sharply with investor-funded businesses that may accumulate bloat without clear purpose.
Flexibility and speed provide bootstrapped startups with significant competitive advantages. Self-funded entrepreneurs don’t need to reach consensus with investors before acting, enabling them to pivot quickly based on market feedback. This agility aligns exceptionally well with modern software development methodologies that emphasize eliminating waste and delivering quickly. Investor-funded businesses often require lengthy approval processes from investors to pursue opportunities or make decisions, while bootstrapping eliminates this hurdle.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, bootstrapping presents significant challenges that entrepreneurs must carefully consider. Limited resources and capital represent the most obvious constraint, as founders can only invest what they personally possess or generate through business operations. This limitation may restrict expansion opportunities, prevent hiring key talent, or slow growth compared to well-funded competitors. Bootstrapping works best for businesses with low capital requirements or those that can generate revenue quickly.
Personal financial risk increases substantially when entrepreneurs invest their own savings or take personal loans to fund their ventures. Unlike external investors who expect only returns on their investment, bootstrapped founders risk their personal financial security. The business might also lack external validation from professional investors, potentially making it harder to attract customers, partners, or eventual acquirers who view investor backing as a quality signal.
When Bootstrapping Makes Sense
Bootstrapping proves particularly viable for startups with low initial costs, a focus on recurring revenue, and a patient growth plan. Industries with minimal capital requirements or businesses that can achieve profitability quickly are ideal candidates for self-funding. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies, consulting firms, service businesses, and digital products often require less upfront capital than manufacturing or hardware startups, making them well-suited for bootstrapping.
Entrepreneurs who prioritize independence and control often choose bootstrapping over venture capital, allowing them to grow at their own pace without external financial pressure. This approach works especially well for founders who have personal savings available, possess experience in their industry, and feel comfortable with the risks involved in self-funding. Additionally, bootstrapping can serve as a proof of concept, demonstrating business model viability before seeking more substantial external financing.
Bootstrapping Statistics and Success Rates
Research provides mixed signals on bootstrapping success rates. While bootstrapped businesses face resource constraints, they often develop strong financial fundamentals and customer focus that contribute to long-term sustainability. Studies show that first-time startup founders have an 18% success rate, while serial entrepreneurs achieve 20% success rates—suggesting that experience matters more than funding source in many cases.
Bootstrapped companies that survive the early stages often emerge with stronger business models, better unit economics, and more sustainable competitive advantages than their venture-backed counterparts. The financial discipline and customer focus required by bootstrapping can create more resilient organizations, even if growth occurs more slowly.
5. Government Grants and Support Programs: Non-Dilutive Funding
Government grants and support programs represent a unique funding opportunity that provides non-repayable financial assistance to startups without requiring equity dilution or debt repayment. Unlike traditional funding sources, government grants are designed to promote innovation, employment, rural development, technology advancement, and economic growth in sectors the government prioritizes.
Understanding Government Grant Ecosystems
Government grants come in multiple forms, tailored to different needs, sectors, and development stages. In India, the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) offers grants up to ₹50 lakh (approximately $60,000) for early-stage startups, focusing on proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, MVP creation, and market entry. This scheme represents part of a broader ₹1,000+ crore budget allocation for startup support in 2025.
The MSME (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) sector receives substantial government support, with ₹3,900 crore allocated in 2025 for technology upgradation, cluster development, and infrastructure enhancement. The MSME subsidy schemes specifically target tech upgrades and infrastructure development, providing crucial support for businesses operating at smaller scales.
For startups with research, social impact, or innovation angles, programs like SBIR and STTR grants in the United States provide non-dilutive funding from government agencies. Additional options include grants from foundations like The Gates Foundation, corporate programs such as Google for Startups, and university innovation labs. While grants can be time-intensive to apply for, they typically come with no strings attached—no equity dilution, no debt repayment, and no investor control.
Strategic Government Initiatives
Beyond direct grants, governments worldwide have established comprehensive support ecosystems for startups. The SIDBI Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) in India operates with a ₹10,000 crore corpus, providing equity infusion through Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs). This equity-based government funding invests in startups in exchange for ownership stakes, offering substantial capital without traditional debt obligations.
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) provides loans up to ₹10 lakh with no collateral required, organized into three categories: Shishu, Kishor, and Tarun. The Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for MSEs (CGTMSE) offers loans up to ₹2 crore with credit guarantees, ideal for MSMEs and startups needing working capital. For women and SC/ST entrepreneurs, the Stand-Up India Scheme provides loans ranging from ₹10 lakh to ₹1 crore.
The Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE) scheme specifically targets tech startups, providing support for product development and commercialization. Many states including Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Kerala have developed their own grant schemes aligned with local priorities and economic development goals.
Application Process and Eligibility
Applying for government startup funding requires systematic preparation and attention to regulatory requirements. Entrepreneurs should begin by choosing the right funding scheme aligned with their business sector, size, and goals. This requires researching available programs and understanding which schemes best match the startup’s profile and objectives.
Preparing a comprehensive business plan is essential, including revenue models, projected financials, problem-solution fit, innovation potential, and scalability. Startups must typically register on official portals like the Startup India Portal and complete Udyam/MSME registration where applicable. The application process requires submitting detailed documentation including business plans, financial projections, legal certificates, and compliance attestations.
Eligibility criteria generally include specific business structures such as Private Limited Companies, LLPs (Limited Liability Partnerships), and Partnership Firms. Certain grants target specific sectors like technology, agriculture, or traditional crafts, while others focus on demographics such as women entrepreneurs or underrepresented groups. Projects should align with government priorities including innovation, job creation, rural development, or export promotion.
Incubation Centers and Acceleration
Many government grants are now channeled through incubation centers, which support entrepreneurs with mentorship, office space, networking, and access to funding opportunities. Startups apply to incubators with their ideas, and if selected, receive help refining business models and connecting to relevant grant opportunities. The incubator might directly distribute grants or assist with pitching for government funds.
In India, incubation schemes under Startup India support early-stage startups by providing funding, mentorship, infrastructure, and networking opportunities. These programs are organized into categories: G1C centers offer deep support including mentoring, capacity building, and industry linkages; G2C centers facilitate aspiring entrepreneurs and students to build high-quality startups; and G3C centers initiate and evangelize innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystems in unexplored regions.
Global Variations and Trends
Government support for startups varies significantly by region and country. The United States government provides substantial funding through agencies like the Small Business Administration (SBA), offering SBIR/STTR programs that distribute billions annually to innovative small businesses. European countries maintain active grant programs supporting research and development, sustainability initiatives, and technology commercialization.
In emerging markets, government funding plays an increasingly critical role in building startup ecosystems. Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) funding participation in Indian startups is increasing at a rate of 7% year-on-year, complementing traditional government grant programs. This hybrid approach combines direct government support with strategic corporate investment, creating multiple pathways for startups to access non-traditional funding sources.
The approval timeline for government grants typically ranges from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the specific scheme and document verification requirements. Founders should regularly check application status, respond promptly to authority queries, and strictly adhere to scheme-specific compliance norms to maximize approval chances.
Strategic Considerations for Founders
Selecting the optimal fundraising strategy requires careful consideration of multiple factors including growth objectives, industry sector, geographic location, and founder preferences. The statistics paint a sobering picture: only 2-3% of pre-seed applications receive external funding, and less than 1 in 150 pre-seed applications will ever reach Series A funding. These harsh realities underscore the importance of strategic planning and realistic expectations.
Industry and sector considerations significantly impact fundraising success. FinTech attracts substantial funding when successful but faces failure rates up to 75% due to regulatory compliance challenges. Healthcare and biotech show 15% higher five-year survival rates compared to average sectors, reflecting longer development cycles and higher barriers to entry. E-commerce startups face approximately 80% failure rates due to intense competition and challenging unit economics.
Geographic factors also play crucial roles. North America’s dominance in venture capital, capturing 70% of global funding in H1 2025, means startups in the region have greater access to institutional capital but face fiercer competition. European ecosystems are growing, with cities like Paris climbing in global rankings due to AI talent and pro-business government policies. Asian markets show mixed performance, with India emerging as a bright spot while China faces capital pressures.
Founder experience matters more than many entrepreneurs realize. Serial entrepreneurs demonstrate 20% success rates versus 18% for first-time founders—a modest but meaningful difference. Prior funding and lead investors create social proof that significantly improves odds, with the Angel Capital Association noting that “funding rates are higher when there is validation in terms of the presence of a lead investor”. Accelerator experience from reputable programs provides valuable third-party validation and training, improving funding rates even beyond Y Combinator’s exclusive 1% acceptance rate.
The most successful startups often employ a hybrid funding approach, combining multiple sources strategically aligned with their growth stage. Bootstrapping in the early stages to validate product-market fit, then raising angel investment for initial scale, followed by venture capital for aggressive expansion, and supplemented with government grants for specific R&D projects represents a common successful pattern.
Conclusion
The global startup fundraising landscape in 2025 presents both unprecedented opportunities and formidable challenges for entrepreneurs worldwide. With venture capital reaching $120 billion quarterly, AI companies capturing over half of all funding, and alternative financing options proliferating, founders have more pathways to capital than ever before. Yet the statistics remain unforgiving: only 2-3% of startups secure pre-seed funding, less than 10% progress from seed to Series A, and approximately 75% of venture-backed companies never return cash to investors.
Success in startup fundraising requires more than a compelling pitch—it demands strategic thinking, realistic expectations, and willingness to pursue multiple funding channels simultaneously. Venture capital offers substantial resources and expertise for high-growth companies ready to scale rapidly, while angel investors provide crucial early-stage capital coupled with mentorship for pre-seed and seed-stage ventures. Crowdfunding democratizes access to capital and validates market demand, bootstrapping ensures complete founder control and financial discipline, and government grants deliver non-dilutive funding for innovation-focused startups.
The most resilient startups build fundable businesses rather than optimizing solely for fundraising, focusing on strong unit economics, sustainable growth, and genuine customer traction. As the data conclusively demonstrates, external funding remains statistically improbable—but entrepreneurs who understand these five major funding pathways, align their strategies with realistic expectations, and execute with discipline can dramatically improve their odds of securing the capital needed to transform their vision into a thriving global enterprise.
Nitesh
Founder @ GrowthMandi, JobsMandi, StartUpMandi. Working in various Domains since 2017. Like, Sales & Marketing, Website Development, Graphic Designing, Digital Marketing, SEO, Business Development. Hobby: Research & Innovation, Photography, Travelling, Cooking.